3. The foxBMS 2 Platform
The foxBMS 2 platform consists of two main elements:
the foxBMS BMS-Master and
the BMS-Slaves.
The foxBMS BMS-Master consists of 2 boards:
the BMS-Master,
the BMS-Interface.
Optionally the foxBMS BMS-Master can be extended with the BMS-Extension.
An ARM-based microcontroller (Cortex-R5) is used on the foxBMS BMS-Master.
The foxBMS BMS-Master communicates with the outside world via a CAN bus. The current flowing through the battery system is measured via a current sensor connected to a CAN bus. The current sensor is controlled via CAN by the foxBMS BMS-Master and sends the resulting measurement via CAN.
The BMS-Slaves (based on BMS-Slaves) are used for measuring cell voltages and cell temperatures, as well as for passive balancing in battery modules. The BMS-Slaves can be connected in series as a daisy-chain.
In order for the foxBMS BMS-Master to communicate with the BMS-Slaves, a BMS-Interface is needed. It implements the physical layer of the communication between the foxBMS BMS-Master and the BMS-Slaves.
Control requests to the foxBMS BMS-Master are made via CAN messages. They control the externally facing BMS behavior of the system such as opening and closing the contactors. This behavior based on the internal implementation and application dependent. The foxBMS BMS-Master monitors the state of the battery system to ensure a safe operation of the system. The measurement data and all relevant information of the system is communicated through a CAN interface to a superior control unit.
The foxBMS BMS-Master also provides an interlock line that is closely monitored. This fast acting interface that can be connected through crucial system components such as the foxBMS BMS-Master, emergency stop switch, service disconnect switches, high voltage connectors and similar devices. The interlock line can be opened by any connected device. It is possible to define a system behavior in the case that the interlock line has been opened such as the transition to an application-specific safe-state. In the default implementation, all contactors will be opened and the BMS will switch to an error state.
See Fig. 3.1.
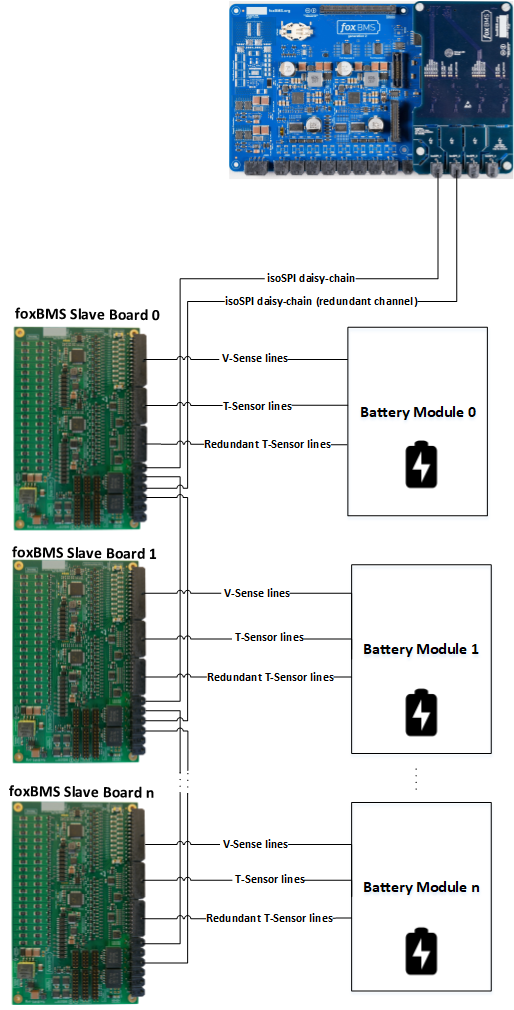
Fig. 3.1 High level overview of foxBMS 2
In case that an application requires more inputs, outputs or specific hardware functions, these can be implemented through a BMS-Extension. This is a specialized board that connects through a set of connectors to the foxBMS BMS-Master and can implement application-specific hardware.
This description reflects the current state of foxBMS 2. Due to the open nature of the system, many other possibilities can be implemented, like for example:
Use of other types of current sensors (e.g., shunt-based or Hall-effect based)
No BMS-Slave needs to be used: a direct measurement of the cell voltages and cell temperatures can be performed by the foxBMS BMS-Master
A higher number of contactors can be controlled (e.g., up to 9)
etc…
